Ethereum Classic is a hard fork from Ethereum that took place in summer 2016 after the DAO hack. Thus Ethereum Classic shares a lot of similarities with Ethereum. But where are the differences and how did the infamous Ethereum Classic Hard Fork come about? To better explain what Ethereum Classic is, we will take a look at history and show you what the DAO was and what the consequences of the hack were.
The DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization)
The Ethereum Network went live with Frontier on 30 July 2015. A little later, in March 2016, the Homestead version followed. Both versions of Ethereum allowed developers to create Smart Contracts and run them on the Ethereum blockchain.
The DAO started on 30 April 2016 with the publication of its website and a 28-day crowdsale. It was a decentralised venture capital fund set up to revolutionise the way venture capital is distributed. The DAO was practically a venture capital company without a traditional management or board of directors deciding on the projects to be supported.
Instead, investors were able to purchase DAO tokens under the Crowdsale token and thus buy themselves a voting right when it came to investment decisions for projects. The fund could have financed all new, decentralised applications that would have been developed on the Ethereum blockchain.
The Crowdsale was a complete success. In the 28 days, the DAO project was able to collect a legendary amount of 11.5 million ether (about 150 million US dollars). The largest single investor held less than 4% of all DAO tokens, so there was no centralization in one person.
The DAO Hack
However, the hyped and promising project failed shortly after its launch. On 17 June 2016, the DAO was hacked for a combination of vulnerabilities. The hacker exploited a vulnerability in the DAO program code (not in the Ethereum protocol) that had become public a month earlier. The hacker stole about 3.6 million ethers (about 50 million US dollars).
The DAO was then closed. Many investors threatened to lose their entire investment. The Ethereum price fell from $20 to $13 due to bad news. In order to regain investor confidence, the Ethereum community had to make a tough decision. Either the developers would follow the “code is law” standard, which would not reverse the 3.6 million ether hack. On the other hand, it was possible to perform a hard fork and invalidate the “old” part of the hacker’s blockchain. The core development team of Ethereum, around Vitalik Buterin, decided after long discussions for a hard fork. Thus the stolen ethers could be returned to the owners.
However, the decision also met with harsh criticism within the Ethereum community. According to the standard “Code is law”, the idea of a Hard Fork was perceived as unethical by some members. After all, everything that happens on the blockchain should be unchangeable.
But finally the Hard Fork was implemented. The “old” Blockchain became Ethereum Classic. Around 90 percent of the new Ethereum blockchain followed. However, at least 10 percent of the miners joined Ethereum Classic.
What is Ethereum Classic?
Ethereum Classic (ETC) is thus an open source blockchain that is largely based on today’s Ethereum protocol. Therefore it has the same functionalities (Smart Contracts, decentralized Apps) as Ethereum.
ETC is the official token of the blockchain to pay the transaction fees or users for services.
Comparison: Ethereum vs. Ethereum Classic
However, there are also differences between ETH and ETC. While Ethereum has no hardcap, ECIP 1017 (Ethereum Classic Improvement Proposal 1017) has set the total amount of Ethereum Classic at ETC 210 million. Due to fluctuations in ETC’s compensation rate, the ETC developer community expects a maximum total offer that will not exceed ETC 230 million.
Another difference is the Ethereum Mining Reward. The base reward was redefined with the new monetary policy in February 2018 and has been dependent on the block number ever since. Every five million blocks (approx. 2.4 years), the base reward decreases by 20%. Originally it was 5 ETC. With block number 5.000.000 the “Base Reward” was changed to 4 ETC. It is expected to drop to 3.2 ETC for block number 10,000,000 in April 2020.
In addition, as with Ethereum, there is the “Uncle Reward“. This depends on the number of uncle blocks contained and amounts to an additional 3.125% of the basic reward (currently: 0.125 ETC). From about April 2020, the “Uncle Reward” will be set to 0.1 ETC.
Another difference is that Ethereum plans to switch from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake (with Casper). Ethereum Classic, on the other hand, has not yet declared its intention to switch to proof-of-stake and will therefore also be of long-term interest to ETH miners.
In the end, Ethereum has been more successful than ETC after the DAO hack. Ethereum has practically become the standard for ICOs and dApp developments, while Ethereum Classic could only host very few ICOs.
Ethereum Classic Roadmap
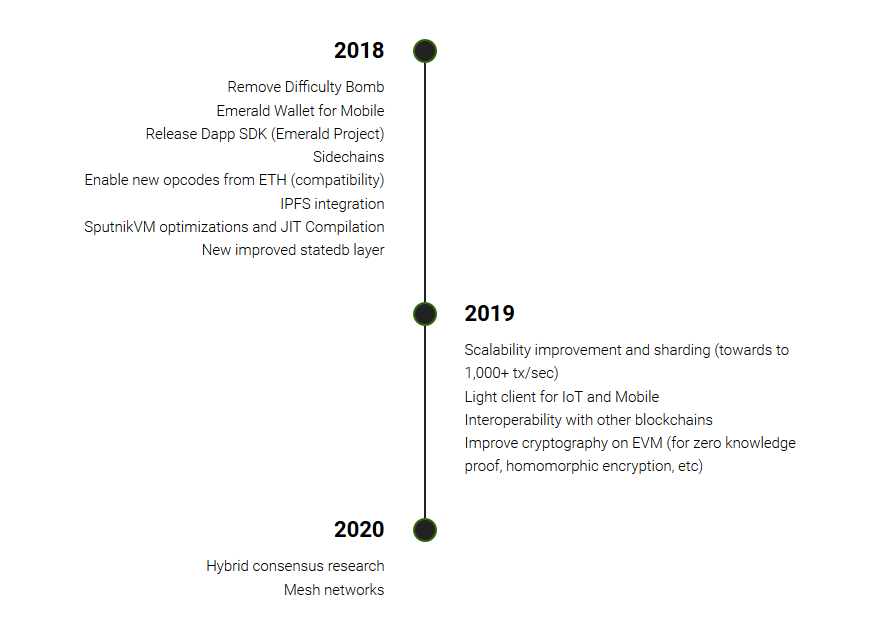
However, Ethereum has a promising roadmap. In September 2018, Ethereum Classic (ETC) announced the release of its Software Development Kit (SDK) for the development of distributed applications (dApps). Callisto, a separate blockchain that also serves as sidechain for Ethereum Classic, was also released in 2018. In 2019, the scalability of Ethereum Classic will be increased to over 1,000 transactions per second.
Subscribe to our daily newsletter!
No spam, no lies, only insights. You can unsubscribe at any time.




